Deploying a .NET Core AWS Lambda function from VS2019
To use Visual Studio 2019 for AWS Lambda development, you will need the AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio. It works like a charm, though the new project wizard could use a cleaner and fresh UI.
After the installation of the Toolkit, the project templates show up nicely in the Add new project window.
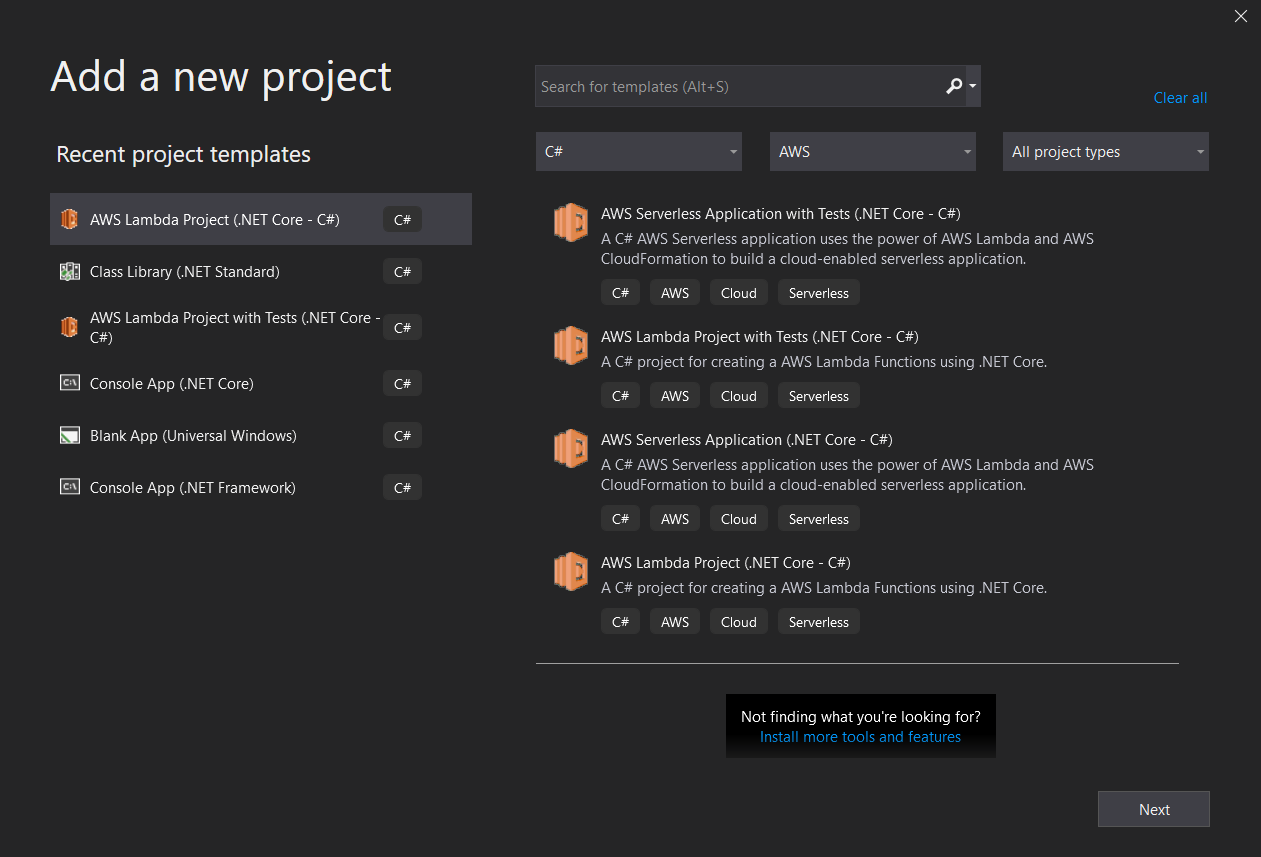
Then you are led to the wizard to select the blueprint. My first attempt at it, I chose Empty Function.
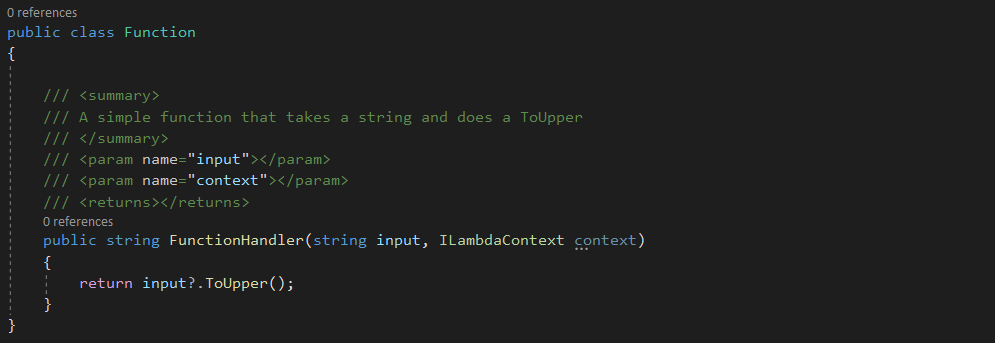
The next thing to do right after this is rename your function. Make sure you update the reference in aws-lambda-tools-defaults.json for the property function-handler.
With the Toolkit installed, right clicking the project will show you the “Publish to AWS Lambda” option. The first time you do this, you will have to set up your AWS credentials. You will likely need AWS CLI tools to set this up. From then on, you will get this screen.
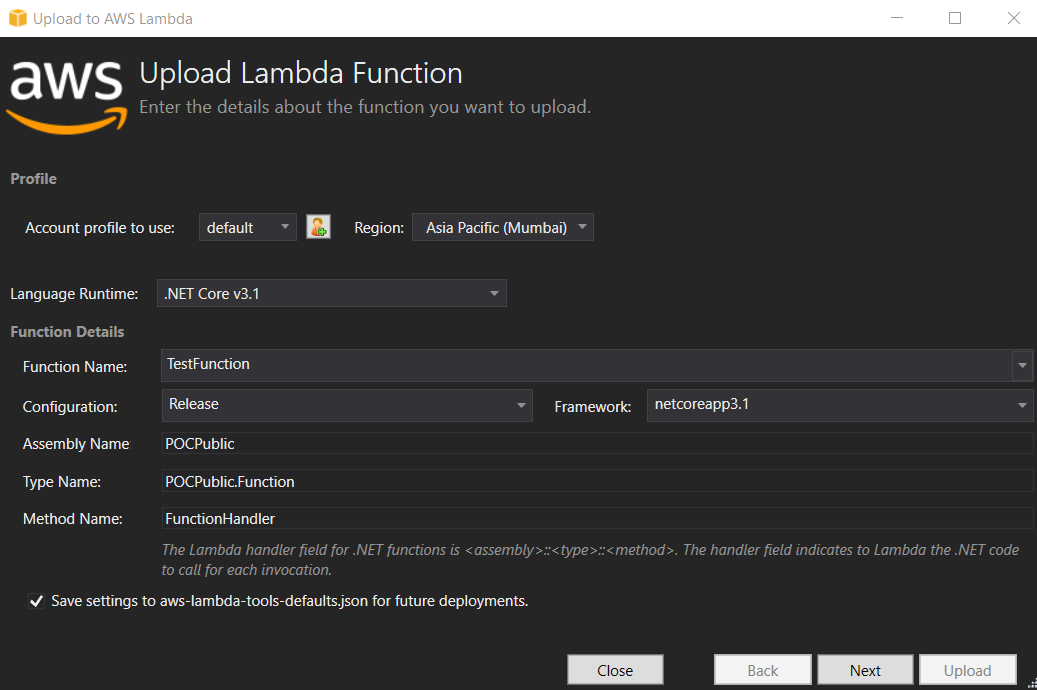
Other than the Function Name, everything else will be taken from your default settings.
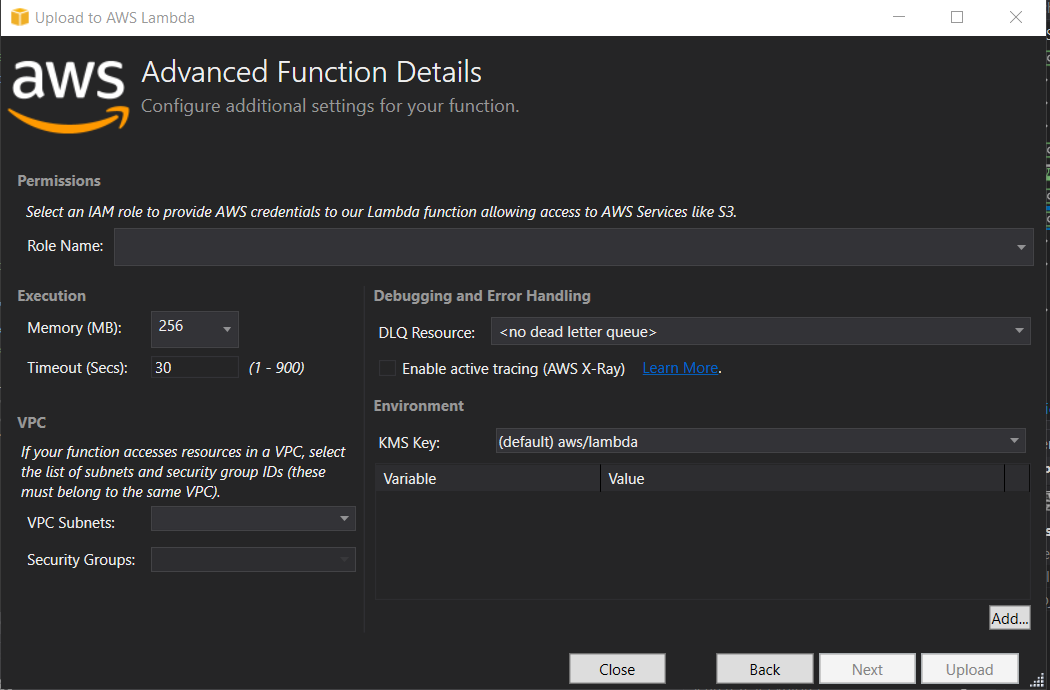
After selecting the Role Name, you can Upload the function and it opens the log view of your function being uploaded. By default, the Function invoker UI is also opened.
When you invoke your function, you will probably encounter this error message. You will get this error message, no matter what input you specify, or if you specify an input at all.
{
"errorType": "JsonSerializerException",
"errorMessage": "Error converting the Lambda event JSON payload to a string. JSON strings must be quoted, for example \"Hello World\" in order to be converted to a string: The JSON value could not be converted to System.String. Path: $ | LineNumber: 0 | BytePositionInLine: 1.",
"stackTrace": [
"at Amazon.Lambda.Serialization.SystemTextJson.DefaultLambdaJsonSerializer.Deserialize[T](Stream requestStream)",
"at lambda_method(Closure , Stream , Stream , LambdaContextInternal )"
],
"cause": {
"errorType": "JsonException",
"errorMessage": "The JSON value could not be converted to System.String. Path: $ | LineNumber: 0 | BytePositionInLine: 1.",
"stackTrace": [
"at System.Text.Json.ThrowHelper.ReThrowWithPath(ReadStack& readStack, Utf8JsonReader& reader, Exception ex)",
"at System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.ReadCore(JsonSerializerOptions options, Utf8JsonReader& reader, ReadStack& readStack)",
"at System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.ReadCore(Type returnType, JsonSerializerOptions options, Utf8JsonReader& reader)",
"at System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.ParseCore(ReadOnlySpan`1 utf8Json, Type returnType, JsonSerializerOptions options)",
"at System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.Deserialize[TValue](ReadOnlySpan`1 utf8Json, JsonSerializerOptions options)",
"at Amazon.Lambda.Serialization.SystemTextJson.DefaultLambdaJsonSerializer.Deserialize[T](Stream requestStream)"
],
"cause": {
"errorType": "InvalidOperationException",
"errorMessage": "Cannot get the value of a token type 'StartObject' as a string.",
"stackTrace": [
"at System.Text.Json.Utf8JsonReader.GetString()",
"at System.Text.Json.Serialization.Converters.JsonConverterString.Read(Utf8JsonReader& reader, Type typeToConvert, JsonSerializerOptions options)",
"at System.Text.Json.JsonPropertyInfoNotNullable`4.OnRead(ReadStack& state, Utf8JsonReader& reader)",
"at System.Text.Json.JsonPropertyInfo.Read(JsonTokenType tokenType, ReadStack& state, Utf8JsonReader& reader)",
"at System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.ReadCore(JsonSerializerOptions options, Utf8JsonReader& reader, ReadStack& readStack)"
]
}
}
}
I tried fixing this error by using Newtonsoft.JSON instead of the default serializer provided by the SDK. However, it changed nothing.
The issue is with the Function and its function parameters.
You have to change string datatype of input
public string FunctionHandler(string input, ILambdaContext context)
into object datatype.
public string FunctionHandler(object input, ILambdaContext context)
Thats it, its fixed. You will have to handle the serialization and deserialization yourself.
